Table of Contents
Pregnancy is often seen as a joyous and exciting time in a woman’s life. The anticipation of new life, the promise of motherhood—it’s a time filled with hope and dreams. But sometimes, pregnancy takes an unexpected turn. This is where the concept of an ectopic pregnancy enters the picture—a condition that demands our understanding and awareness.
In this blog, we’ll explore what ectopic pregnancy is, its causes, symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, and treatment options to help you better understand this challenging condition.
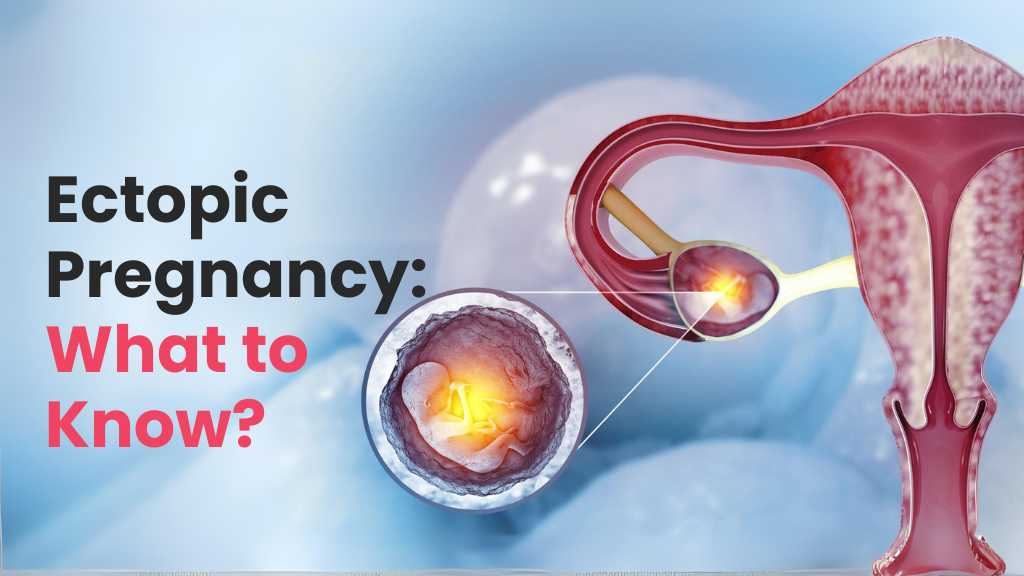
What Is Ectopic Pregnancy?
Typically, a fertilized egg attaches itself to the lining of the uterus, where it can grow into a healthy baby. However, in the case of an ectopic pregnancy, this process goes awry. The fertilized egg attaches and starts growing outside the uterus, in areas like the fallopian tube, ovaries, abdomen, or the lower part of the cervix. In most instances, about 90%, the egg attaches to a fallopian tube, leading to what is known as a tubal pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancies are relatively rare, accounting for approximately 1 in 50 pregnancies in the United States. However, it’s crucial to recognize the seriousness of this condition. If left untreated, ectopic pregnancies can lead to life-threatening complications, making them the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the first trimester.
Can a Baby Survive an Ectopic Pregnancy?
Unfortunately, an ectopic pregnancy is not “viable.” This means that the fertilized egg cannot develop into a baby that can survive either inside or outside the body. The egg lacks the necessary blood supply and support required for growth outside the uterus, inevitably resulting in a pregnancy loss.
Signs and Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Early signs of ectopic pregnancy can mimic those of a normal pregnancy, making it challenging to diagnose in its early stages. Symptoms such as a missed period, breast tenderness, and abdominal discomfort may be present. However, only around half of women with an ectopic pregnancy will experience all three main signs: a missed period, vaginal bleeding, and belly pain.
Other early signs to watch for include:
- Upset stomach and vomiting
- Sharp belly cramps
- Pain on one side of your body
- Dizziness or weakness
- Pain in your shoulder, neck, or rectum
If you experience severe ectopic pregnancy symptoms such as heavy vaginal bleeding with lightheadedness, fainting, shoulder pain, or intense belly pain, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention, possibly by calling 911 or heading to the nearest hospital.
When Does Ectopic Pregnancy Pain Start?
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy usually manifest between the 4th and 12th weeks of pregnancy.
Ectopic Pregnancy Causes and Risk Factors
Determining the exact cause of an ectopic pregnancy can be challenging, but certain factors can increase your risk. These include:
- Smoking cigarettes
- Being older than 35
- Having a sexually transmitted infection
- Scarring from pelvic surgery
- A history of a previous ectopic pregnancy
- Attempts to have tubal ligation or its reversal
- Undergoing fertility treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF)
- Becoming pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD) for birth control
Complications in Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy, a condition where a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the uterus, can lead to several complications. The most critical of these is the rupture of the fallopian tube, which can result in severe internal bleeding and requires immediate medical intervention. Even before rupture, internal bleeding into the abdominal cavity can occur, causing symptoms like abdominal pain and dizziness. In some cases, this bleeding can lead to shock, a life-threatening condition.
Ectopic pregnancies are also associated with the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which is an infection of the reproductive organs. Surgery to treat ectopic pregnancy can lead to pelvic adhesions and scarring, potentially affecting future fertility. On an emotional level, coping with the loss of a pregnancy and the potential complications can be challenging. Additionally, having one ectopic pregnancy increases the risk of experiencing another in the future, necessitating close monitoring during subsequent pregnancies to ensure they are located in the uterus. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent severe complications in ectopic pregnancies.
Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosis
Diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy typically involves a combination of tests, including a pregnancy test and a pelvic exam. Doctors may also use ultrasound to visualize the uterus and fallopian tubes. This non-invasive procedure uses sound waves to create images of the reproductive organs.
There are two types of ultrasound procedures commonly used for ectopic pregnancy diagnosis: transvaginal and transabdominal. The former is performed using a probe inserted into the vagina, while the latter involves moving a wand over the abdomen. Both aim to detect the presence and location of the gestational sac and assess whether there is a fetal heartbeat.
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Ectopic pregnancy treatment is essential because the condition can be life-threatening if left untreated. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the stage of the ectopic pregnancy, the woman’s overall health, and the severity of symptoms. The main treatment options for ectopic pregnancy are:
- Medical Management: This option is typically chosen when the ectopic pregnancy is detected early and hasn’t yet caused significant damage. It involves the use of a medication called methotrexate, which stops the growth of the embryo and allows the body to absorb it over time. Methotrexate is administered as an injection and may require multiple doses. Follow-up monitoring is crucial to ensure that the treatment is successful.
- Surgical Intervention:
– Laparoscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive surgical procedure is commonly used for ectopic pregnancies. A small incision is made in the abdomen, and a thin, flexible tube with a camera (laparoscope) is inserted to locate and remove the ectopic pregnancy or repair any damage to the fallopian tube. Laparoscopic surgery is preferred when possible, as it allows for a quicker recovery.
– Laparotomy: In cases of severe damage, a larger abdominal incision (laparotomy) may be required to remove the ectopic pregnancy or repair the fallopian tube. This approach is reserved for more complex cases.
- Expectant Management: In some instances, when the ectopic pregnancy is very early and there are no signs of rupture or significant bleeding, a healthcare provider may choose to closely monitor the situation with serial blood tests (hCG levels) and ultrasounds. This approach is considered when it’s believed that the body may naturally resolve the ectopic pregnancy without medical or surgical intervention.
After treatment, it’s essential for the woman to follow up with her healthcare provider for monitoring. This ensures that the ectopic pregnancy has been successfully resolved and that there are no complications or signs of infection.
After an Ectopic Pregnancy
Following an ectopic pregnancy, conceiving a healthy pregnancy may be challenging, especially if a fallopian tube is removed. Consulting a fertility specialist is advisable in such cases. Additionally, it’s essential to discuss with your doctor how long you should wait before attempting to conceive again. Some experts recommend waiting at least three months to allow your body to heal.
It’s worth noting that an ectopic pregnancy increases the risk of future ectopic pregnancies, so it’s crucial to stay vigilant about changes in your body and seek prompt medical attention if you suspect another pregnancy.
How to Avoid an Ectopic Pregnancy
Unfortunately, there is no foolproof way to prevent an ectopic pregnancy. However, certain lifestyle choices can help reduce your risk:
- Use condoms during sexual activity to lower the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease and sexually transmitted infections.
- Avoid vaginal douches, as they have been linked to an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Final Thoughts
While ectopic pregnancies are relatively rare, they can pose serious health risks if not promptly diagnosed and treated. Understanding the signs of ectopic pregnancy, symptoms, and risk factors associated with ectopic pregnancy is essential for early intervention and successful management. If you suspect you may have an ectopic pregnancy or have concerns about your reproductive health, it’s crucial to seek medical advice promptly.





